Cannabis and the Nervous System
| INDEX | |
|---|---|
| Index Article "Cannabis and the Nervous System" | |
Introduction
In this article we are going to discuss the fascinating world of the nervous system and how this is affected by the administration of cannabis.
It could be said that the nervous system is as if it were the director of a large complex and fully coordinated orchestra, which manages to receive, interpret and respond to the different and multiple stimuli from the environment and internal signals, ensuring its correct functioning.
The importance of the Nervous System lies in the fact that it is the responsible for regulating vital functions, from breathing to the complexity of human thought.
In this article we are going to address the incredible and fascinating world of the nervous system and how different components of cannabis (THC and CBD) interact with it, triggering a multitude of effects.
Stay with us and discover the fascinating world of this great conductor!
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system, as we said in the previous section, is that great orchestra conductor that is responsible for coordinating and regulating the different vital functions of the body.
To begin with the great explanation of this world, we first have to emphasize its division:
1. Central Nervous System (CNS)
It is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
Brain: It is the epicenter of neural activity; the seat of consciousness, memory, thinking and decision making. That is, we could think of him as if he were the CEO of a company, the one in charge of directing the entire office.
Spinal Cord: it is the extension of the brain, and it is where all the nerve endings are located. The spine acts as a communication path between the brain and the rest of the human body. That is, we could say that it is the messenger that carries the orders from the brain to the rest of the organism.
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
It is made up of sensory nerves that connect the central system with the organs, extremities and skin. This system is responsible for transmitting sensory information and regulating functions such as breathing, blood pressure or digestion.
We can divide it into:
Peripheral Nerves: It consists of a network of peripheral nerves that extend from the spinal cord and brain to all parts of the body, transmitting bidirectional information. That is, they are like the telephone lines that connect everything, the calls and messages that keep the boss informed about what is happening.
Ganglia: Groups of nervous cell bodies outside the CNS that participate in the processing of sensory and motor information. That is, they would be like the stations outside the city of the central nervous system, where the information makes a stop to be processed before continuing its journey.
But, what are the most important functions performed by the Nervous System?
1. Control and Coordination
It is responsible for regulating and coordinating all bodily functions, from automatic functions (breathing and heart rate) to voluntary actions (movement and facial expression). That is, it would be like the boss who makes everything work correctly.
2. Perception of the Environment
It is responsible for allowing perception and response to stimuli in the environment, through the senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch). Thanks to this, a person is able to perceive, for example, pain.
3. Thought and Emotion
It is responsible for facilitating higher cognitive processes, including thinking, memory, learning and emotional responses. That is, it is like the master brain that stores all the important information.
4. Muscle Movement
It is responsible for controlling the contraction and relaxation of muscles, allowing movement and coordination. That is, it is as if the muscles were puppets and the nervous system was the puppeteer who makes them dance.
5. Homeostasis
It is what contributes to maintaining the internal stability of the body (homeostasis) by regulating factors such as body temperature, fluid balance and blood pressure. That is, it is the one who works so that everything is in order, the one who tells you when you have to rest, sweat...etc.)
In summary, we can conclude that the nervous system is the great master conductor that directs the orchestra of the organism, ensuring that all parts of the body play in symphony.
Brief introduction of Cannabinoid Receptors and how they intervene in the Central System
As we already mentioned in the Article “Meet Raphael Mechoulam: Endocannabinoid System” our body naturally produces a set of cannabinoids essential for our health.
Cannabinoid receptors are key components of the endocannabinoid system, a signaling system that plays a crucial role in the regulation of various physiological and neuropsychological functions. Imagine that cannabinoid receptors are like special locks on the doors of your cells, and those locks are designed to fit into very specific locks, cannabinoids (chemicals found in the cannabis).
There are two main types of cannabinoid receptors:
CB1 Receivers
They predominate in the Central Nervous System, especially in the brain. These receptors are responsible for the release of neurotransmitters, taking charge of mental and physiological processes (memory, cognitive processes, motor coordination, pain perception...)
When these receptors are activated, they modulate the release of neurotransmitters, including inhibiting GABA release and stimulating dopamine release, contributing to the psychoactive effects associated with THC consumption.
CB2 Receivers
They are distributed, for the most part, in peripheral tissues and in the cells of the immune system. They play a role in modulating the body's immune response, inflammation, and homeostasis.
Its activation is associated with the modulation of inflammatory responses and the regulation of immune function.
Although their presence in the Central Nervous System is less than that of CBQ receptors, it has been shown that they also play a role in neuroinflammation and neuroprotection.
Imagine that there are two locks in the body: doors CB1 and CB2. CB1 locks are found mostly in the brain and CB2 locks are throughout the body.
Interaction of THC and CBD in the Nervous System
Imagine that both THC and CBD are special guests using special keys to open the cannabinoid locks. THC really likes the CB1 gate in the brain, while CBD has a preference for the CB2 gate in other parts of the body.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) binds mainly to CB1 receptors and acts as an agonist that mimics the action of endocannabinoids produced naturally by the body.
This interaction with CB1 receptors in the brain is what causes psychoactive effects (altered perception, increased appetite (See Article Beyond the High: Unraveling the Links between Cannabis, Hormones and Appetite) and memory modulation).
In addition to psychoactive effects, THC may also have analgesic properties by modulating color perception through its interactions with the endocannabinoid system.
When THC opens the CB1 gate, it starts sending messages to nerve cells in the brain, like it's sending exciting emails. Therefore, it can affect mood, time perception and coordination.
Basically the brain is having a party and the CB1 doors are the main entrances. When THC hits, the locks open, and the music (nervous messages) becomes more intense. People (nerve cells) begin to dance in unusual ways, affecting perception and mood.
Unlike THC, CBD has a lower affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Its mechanism of action is complex. Its action is based mainly on the direct activation of these receptors.
CBD modulates the activity of the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting enzymes that degrade endocannabinoids. This results in increased levels of anandamide, an endocannabinoid associated with mood regulation and pain perception.
In addition, it influences various signaling systems, such as the serotonergic system, TRPV1 receptors and adenosine receptors. This wide variety is what contributes to its diversity of effects, including anxiolytic, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties.
Likewise, Cannabidiol can mitigate some of the adverse effects of THC by partially antagonizing CB1 receptors, thus counteracting the intensity of the activation of these receptors by THC.
CBD, furthermore, does not produce significant psychoactive effects.
When CBD uses the CB2 door key, it communicates more with the cells of the immune system and other parts of the body. It is as if he is sending reassuring messages to those in different departments outside the central office.
While THC opens the CB1 door, CBD is more in the side doors (CB2) sending messages to other places in the party. He may not change the music but he is busy making other important elements of the party feel comfortable, relaxed and in balance.
CBD & THC Comparative Table
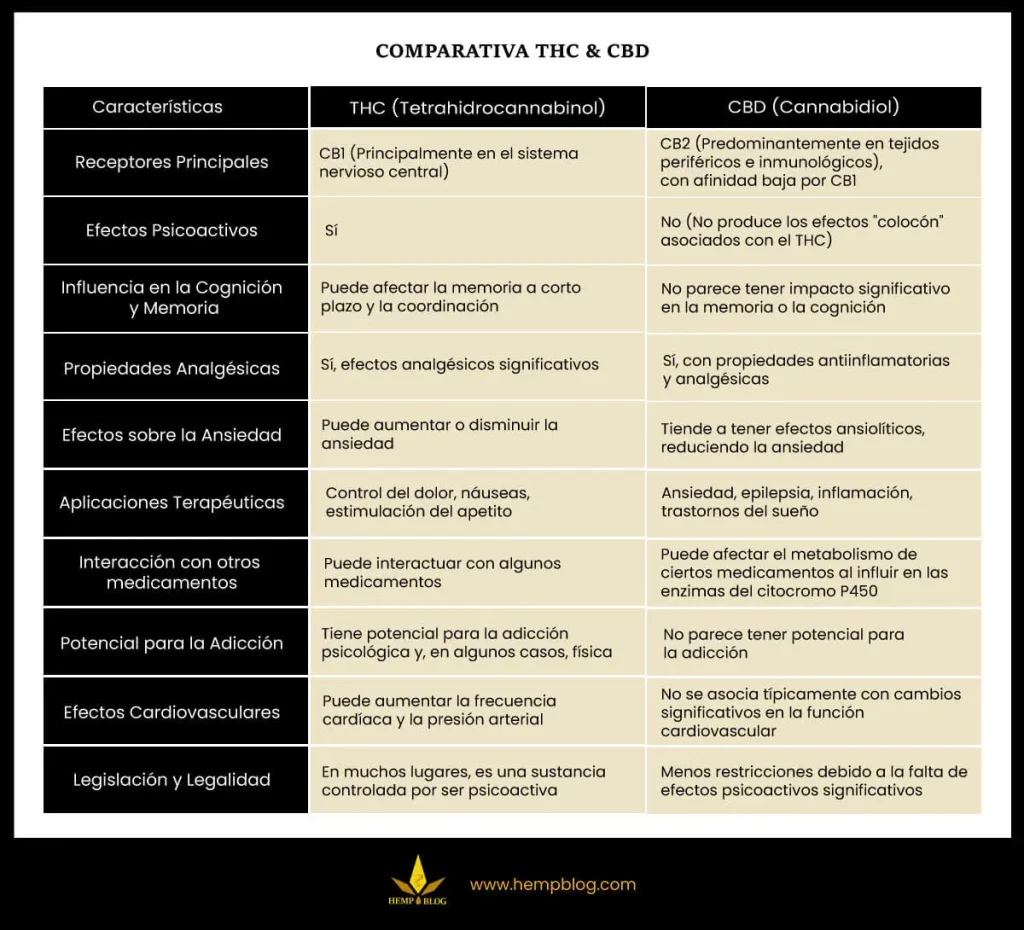
Note: Individual effects may vary depending on dosage, genetics, health status and other factors. Consultation with a health professional is recommended before starting any cannabinoid treatment.
Medicinal and Therapeutic Applications of THC
Chronic Pain: Effective analgesic properties in the management of chronic pain.
Appetite Stimulation: Stimulates appetite, useful in patients with loss of appetite due to medical treatments.
Nausea and Vomiting: Effective in reducing nausea and vomiting, especially in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Muscle Spasms: It can reduce muscle spasms in conditions such as multiple sclerosis.
Glaucoma: It can reduce intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma.
Sleep Disorders (at specific doses): In low doses, it can help you fall asleep.
Psychoactive Effects: Provides psychoactive effects, which may not be desirable in all patients.
Medicinal and Therapeutic Applications of CBD
Anxiety and Stress:
Anxiolytic properties; helps reduce anxiety and stress.
It may be useful in anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Improve the person's mood and relaxation by fighting diseases such as depression, anxiety and stress. Some studies have shown that they help end anxiety because, like any anxiolytic or antihistamine, they activate the CB1 receptor.
Epilepsy: Effective in the treatment of certain types of epilepsy, such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome.
Pain and Anti-inflammatory:
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
It can be used for the management of chronic pain, arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
Sleep disorders:
Contributes to improving sleep quality.
It can be beneficial in cases of insomnia, since it regulates the sleep cycle, favoring the onset, hours of continuity and increased deep sleep.
Neuroprotection:
Protect nerves from acute injuries such as head trauma, strokes and chronic injuries such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Relieve diseases such as amyoatrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's, Huntington's disease... This is because cannabinoids have antioxidant, neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory activities.
Reduce the effects of people who suffer from epilepsy, even making seizure states disappear.
Psychiatric Disorders:
Possible usefulness in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.
Combat antipsychotic episodes since it has anticonvulsant properties.
Control of Nausea and Vomiting: It can help reduce nausea and vomiting associated with medical treatments such as chemotherapy.
Epasticity Reduction: helping to relieve people who suffer from diseases such as multiple sclerosis, a disease that damages the central nervous system (CNS) through inflammatory and degenerative processes producing a severe physical and mental disability and directly affecting their quality of life.
Final conclusion
In summary, it could be said that more and more positive effects are being found. Until now, it has been demonstrated through a multitude of studies that cannabinoids can be a key factor in various areas:
Medicinally it can be used as: antioxidant, antispasmodic, analgesic, neuroprotective and antitumor.
To combat diseases such as: anxiety, stress, depression, arthritis, fibromyalgia, chronic pain, inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's.
Palliatively for cases of: chemotherapy, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, physical pain, acne, dermatitis, psoriasis.
Improve neurological disorders and neuropsychiatric diseases: Parkinson's, dementia, Alzheimer's, ADHD, PTSD, schizophrenia, autism, anxiolytic, antipsychotic, antiepileptic, alcoholism...